Welcome to AI Untangled! In this edition, we're plunging into the fascinating world of AI's breakthroughs in medicine and examining what we can anticipate from large language models like GPT in the near future.
In This Issue
AI in Medicine
Recent Results from AI Testing ←TL;DR jump here
The Future
🤯 AI Breakthrough of the Week!
AI in Medicine
AI has been utilized in medicine for several decades, with some of the earliest applications dating back to the 1970s. One such early example was the MYCIN system, developed at Stanford, designed specifically for diagnosing bacterial infections.
In more recent years, the use of AI in medicine has expanded significantly. AI now finds its application in a wide range of areas within healthcare. However, it's worth noting that these applications represent narrow AI. They can only perform very specific tasks.
Currently, researchers are in the nascent stages of testing more advanced, generalized language models like GPT-4 to explore their potential impact in medicine. As we delve into the research findings presented below, remember that these models are improving at a swift pace.
Recent Results
There are a ton of recent articles on AI in medicine! Good news, we have sifted through them and bring you the most interesting ones we could find.
Medical Boards
This year, researchers from Microsoft and OpenAI evaluated GPT-4’s abilities in medicine. They administered the medical boards (USMLE) and other tests to GPT-4, and here is what they found.
“Our results show that GPT-4 ... exceeds the passing score on the USMLE by over 20 points...“
Impressive, right? GPT-4 scored 84% (to pass you need to score approximately 60% or above.) But the story gets even better. Despite not having access to image-based questions often provided to assist test-takers, GPT-4 managed to score over 70% on those questions.
You can see the paper, published April 12th, here.
Neurosurgery Self-Assessment Exam
In another test, designed for neurosurgeons, GPT-4 outperformed its competition (Google’s Bard AI and GPT-3.5). The exam named SANS (Self-Assessment in Neurological Surgery) is used to prepare for the neurosurgery oral boards examination. And the result?
“On a question bank of predominantly higher-order management case scenarios ... GPT-4 achieved a score of 82.6%...”
Published April 12th on the MedRxiv site, you can view it here.
Interacting with Patients
Now, you may be wondering, “Sure, it's a computer, and it excels at tests. But can it empathize with patients?”
Surprisingly, the answer is yes – and it does so even better than many doctors.
This study looked at patients’ questions and doctors’ answers from an online Q&A community, where moderators ensured that answers originated from credentialed physicians.
In a blind test, health care professionals were asked to gauge both the physicians' and GPT's responses according to their accuracy and empathy.
These graphs tell the story:
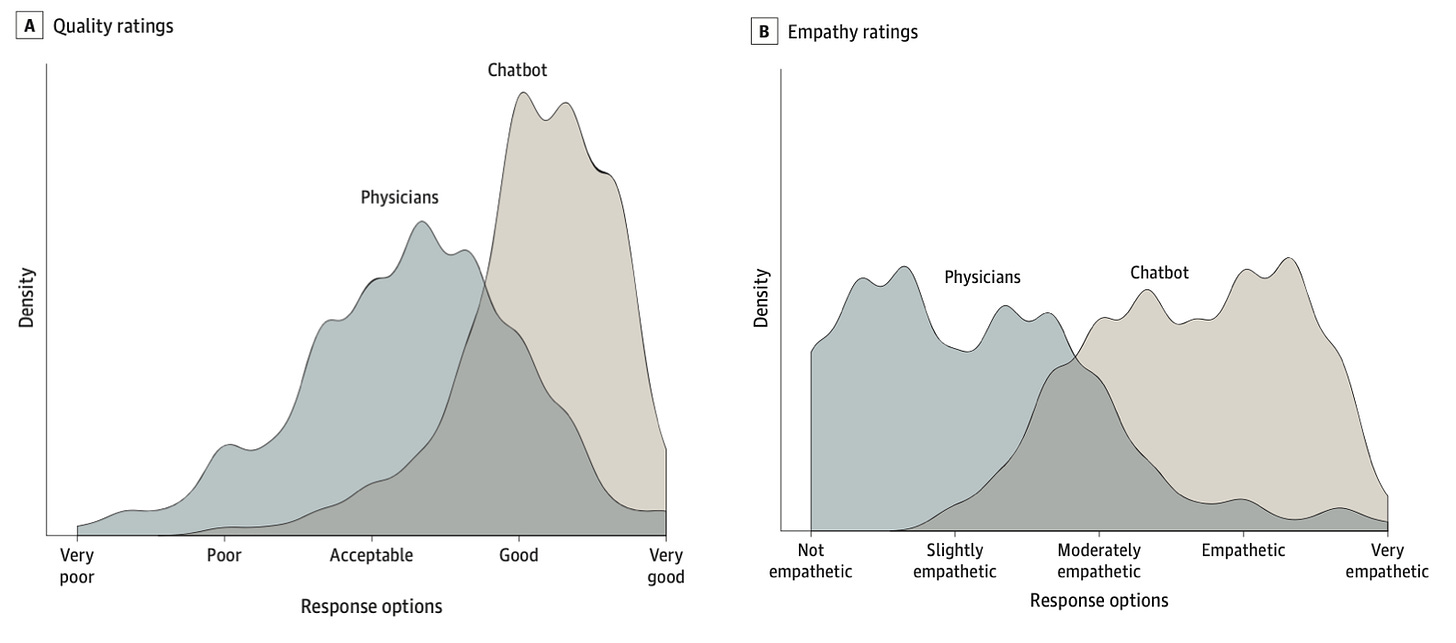
ChatGPT was not only more accurate, it was accurate more often. Further, it was dramatically more empathetic. It was ten times more likely to be rated “moderately empathetic” to “very empathetic” when compared with the doctors’ responses.
“The panel of healthcare professional evaluators preferred ChatGPT responses to physician responses 79% of the time.“
This study was published in the Journal of the American Medical Association on April 18th. You can see it here.
These and other studies illustrate the imminent potential of AI as a comprehensive tool not only for doctors, but also for patients and administrators.
The Future
In the next few years, we'll likely witness a paradigm shift in healthcare, one where AI is integrated into every step. From scheduling appointments, to recommending tests, answering questions, interpreting results and providing diagnosis - AI will prove to be an invaluable tool for doctors as they perform their work.
There is still plenty to figure out. Areas such as reliability, privacy, and bias (among others) will need to be addressed. Though the challenges of implementing AI in healthcare are real, the potential benefits are monumental. Just read the next section to be convinced.
🤯 AI Breakthrough of the Week!
Okay, this is going to be hard to believe, but we have the receipts. This week's breakthrough aligns perfectly with our current topic: medicine.
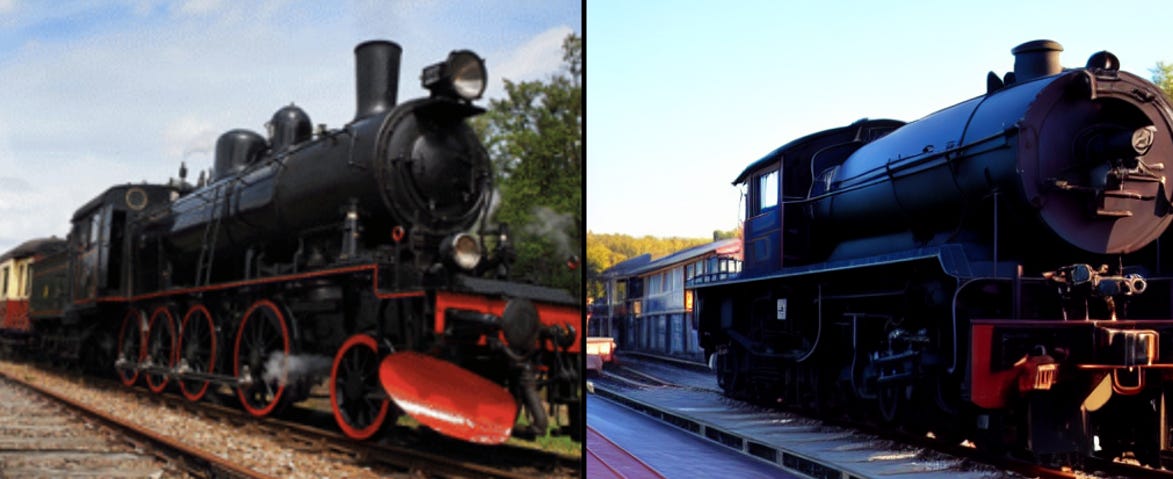
Scientists have developed an AI tool with a remarkable capability. It can analyze MRI scans of a person's brain and then reconstruct an image of what that person was seeing. It's as if the AI is peering into the person's mind and painting a picture of their visual experience.
Below, the first image was shown to a subject who was in an fMRI machine. Following this, the machine generated a scan of the subject's brain which was then handed over to the AI. Using this scan the AI then created the second image.
You can see the paper and more examples here. Several of the authors of the paper are from the Princeton Neuroscience Institute.
Thanks for reading AI Untangled. If you like what you are seeing, share it! We respond to all your feedback, so leave a like or a comment.




